rocksdb笔记
rocksdb 读写
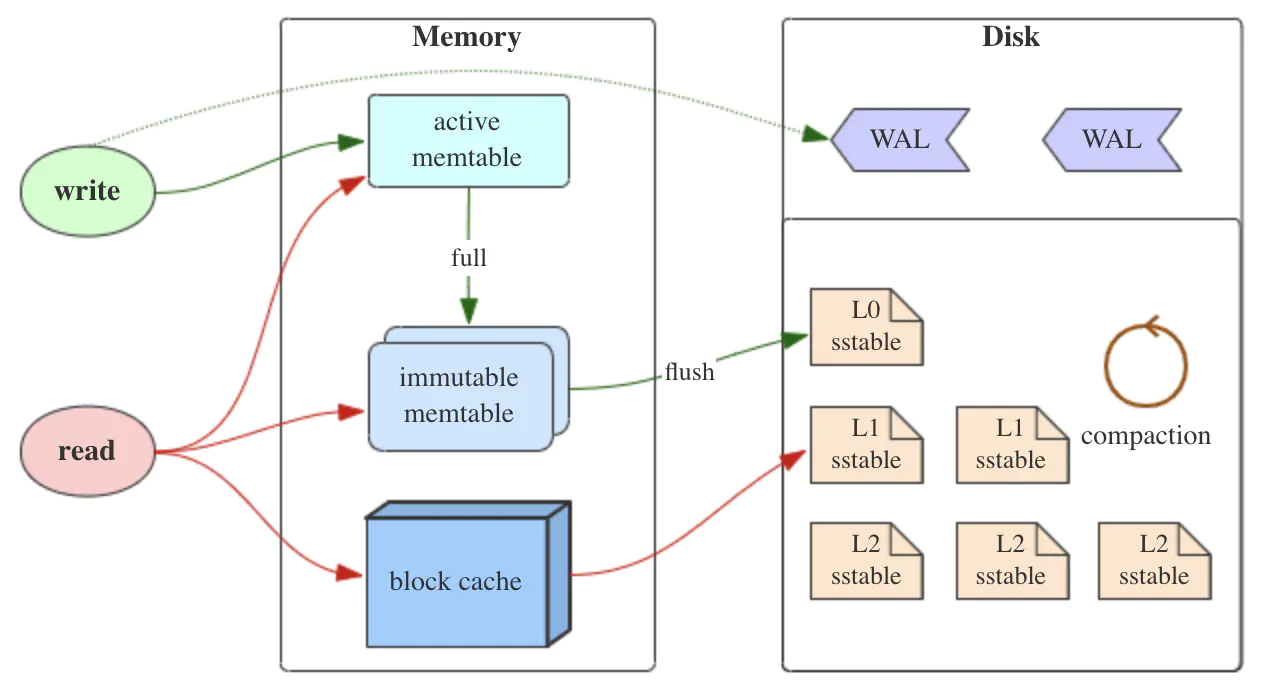
wal: write ahead log it can be used to completely recover the data in memtable
Options::wal_dir: the directory to store wal files Options::wal_ttl: the timeout to delete the wal file
- memtable: the write cache of rocksdb
block cache: the read cache of rocksdb