读书笔记 effective modern c++
判断一个表达式是lvalue or rvalue
A useful heuristic to determine whether an expression is an lvalue is to ask if you can take its address. If you can, it typically is. If you can’t, it’s usually an rvalue.
一般情况下, 可以根据以上所述进行判断。
关于exception safe
如果一个函数是exception safe的,则它表示提供basic exception safety guarantee ,至少要保证:即使函数有exception抛出,pragram invariants remain intact(比如: 没有数据结构出错) and no resources are leaked 如果函数提供strong exception safety guarantee, 则保证:if an exception arises, the state of the program remains as it was prior to the call.
decltype
int x = 0 x is the name of a variable.
(x) yield an expression more complicated than a name.
2
decltype((x)) ---> int &
获取类型相关
c++ standard:typeid(T).name()
<boost/type_index.hpp> 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
template<typename T>
void f(const T& param)
{
using std::cout;
using boost::typeindex::type_id_with_cvr;
// show T
cout << "T = "<< type_id_with_cvr<T>().pretty_name() << '\n';
// show param's type
cout << "param = "
<< type_id_with_cvr<decltype(param)>().pretty_name()
<< '\n'; ...
}
uniform initialization
T x{} ----> {} is that it prohibits implicit
narrowing conversionsamong built-in type. {} means no arguments, not an empty std::initializer_list
prefer deleted function to private function
1 | class Widget |
c++ special member function generation
- The special member functions are those compilers may generate on their own: default constructor, destructor, copy operations, move operations.
- a default constructor is generated only if the class declares no constructors at all.
- copy constructor & copy assignment operator; declare one doesn't prevent compiler from generating the other
- move constructor & move assignment operator; if your declare one, the compiler prevents the other
- declare copy function, that prevents compiler from generating move function. vice versa.
- move functions are generated for a class only when:
- No copy operation are declared in class
- No move operation are declared in class
- No destructor are declared in class.
destructor now is noexcept and virtual only if a base class destructor is virtual
Member template functions never suppress generation of special member functions.
move operation & std::move() & std::forward()
- classname(classname&& ); it cannot take a const rvalue parameter, when the parameter is a const rvalue it trigger the copy constructor.
- std::move() does cast(cast to rvalue), not moving; it doesn’t even guarantee that the object it’s casting will be eligible to be moved.
- std::forward is a conditional cast: it casts to an rvalue only if its argument was bound to an rvalue.
- Neither std::move nor std::forward do anything in runtime
- type&&(must be just this form) means univeral reference, when it should type deduction.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7template <typename T>
void func(T&& params); //params is a universal reference
Widget w;
func(w); //lvalue w passed to func; the type of params is Widget&(an lvalue reference)
func(std::move(w)) // rvlaue passed to func; the type of params is Widget&&(an rvalue reference)
distinguish universal reference to rvalue reference
just T&&, but in following two context(the presence of type deduction), it is universal reference: 1. parameter in function template 1
2template<typename T>
void func(T&& );void func(const T&&)
- auto declaration
1
auto
smart pointers
- shared_ptr shared_ptr 是普通raw pointer的两倍大小,它通常含有两个ptr,如下图所示:
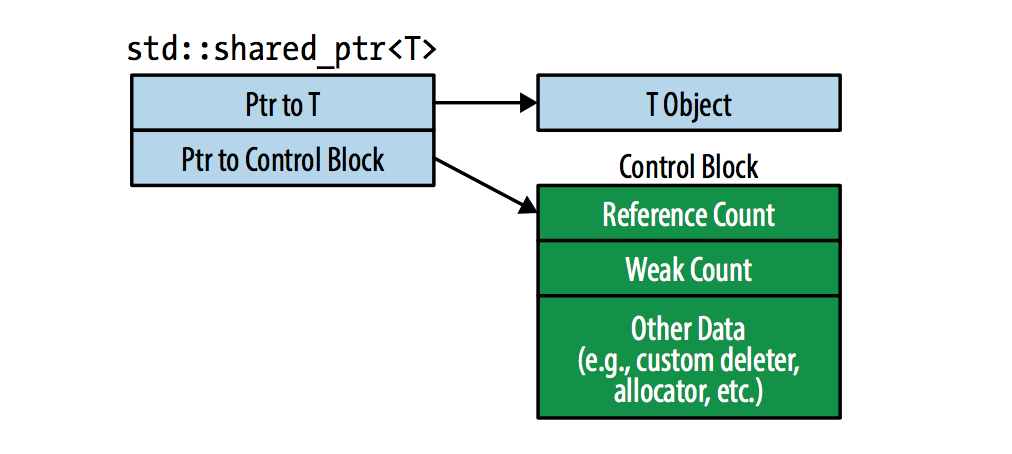 以下三种情况会创建control block:
以下三种情况会创建control block:
- std::make_shared 总是会创建
- 当shared_ptr由unique_ptr构造
- 当shared_ptr由raw pointer构造
- weak_ptr 用于悬浮指针的情况, 可以使用std::weak_ptr::lock成员函数知道其持有的指针是否dangle; 它返回一个std::shared_ptr指针,如果dangle,则返回NULL 可以用一下两个例子说明:
两个shared_ptr指向同个pointer,其中一个shared_ptr被destroy的情况
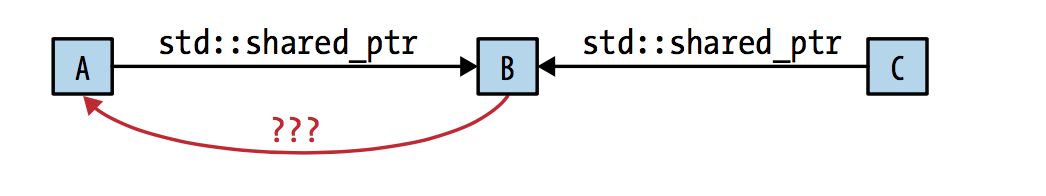 如上图所示:A, C share指向B, B也指向A(此时可用weak_ptr); A指针destroy的情况。
如上图所示:A, C share指向B, B也指向A(此时可用weak_ptr); A指针destroy的情况。observer设计模式中 subjects(状态可能变化的objects)中一般会维护observer的指针数组,这样状态变化时可以通知注册的observer,它对observer的生存期不敢兴趣, 但它对知道其中的哪些observer已经destroy感兴趣, 这样它后面就不需通知这些observer,此时就可用weak_ptr
- unique_ptr unique_ptr比较适用于类中的工厂方法, unique_ptr可以隐式的转化为shared_ptr
reference collapsing
it happens when T& && para or something like this. 1. template instantiation 2. auto 3. typedef or alias 4. decltype
If either reference is an lvalue reference, the result is an lvalue reference. Otherwise (i.e., if both are rvalue references) the result is an rvalue reference.
type related
- the type of an expression is independent of whether the expression is an lvalue or an rvlaue.
1 | class Widget { |
auto tpye deduction is usually the same as template deduction, but auto type deduction assumes that a braced initializer represent as a std::initializer_list and template deduction is not; auto in a function return type or lambda parameter implies template tpye deduction, not auto type deduction.
As a general rule, "invisiable" proxy class doesn't play well with auto. Objects of such classes are often not designed to live longer than a single statement. so should avoid
auto someVar = expression of "invisible" proxy class type;
constexpr
- when applied to object: it is a beefed-up const, which indicates the object is constant and is initialized with value known in compilation time.
- constexpr functions can produce compile-time results when called with arguments whose values are known during compilation.
stack unwinding
The process of removing function entries from function call stack at run time is called Stack Unwinding. In C++, when an exception occurs, the function call stack is linearly searched for the exception handler, and all the entries before the function with exception handler are removed from the function call stack.
Pimpl Idiom(pointer to implementation)
1 | // widget.h |
The Pimpl Idiom is a way to reduce compilation dependencies between a class’s implementation and the class’s clients.
std::is_same, std::decay, std::is_base_of, std::is_constructible, std::declval
- std::is_same judge whether the two type is the same type.
1 | !std::is_same<T, Person>::value |
- std::decay either remove refs, cv-qulifiers or turn array and function types into pointers
1 | std::decay<T>::type |
std::is_base_of<T1, T2> judge whether type T1 is derived from type T2; Types are considered to be derived from themselves
std::is_constructible<T, P> judge is T can be constructed from P as parameter
std::declval
return the reference of T, make call member function possible without through constructor.
make std::thread unjoinable all path
- because when std::thread is joinable, invoke its destructor will cause program termination.
thread communication
- use condition_variable, mutex, bool flag
1 | std::condition_variable cv; |
volatile
- prevent compiler from optimizing the variable; let it load the value of the variable from memory everytime.
- make use of keyword volatile alone is not safe.
multithread
- data race
- one variable -- use std::atomic enough; two or more -- use std::mutex
function(T&&) and function overload
- best not to use together
- tag depatch and std::enable_if technology(effective mordern c++ item27)